


Next: About this document ...
PHYSICS 312.
Midterm. February 10 2003
Allowed aids formula sheet
(2 pages). Calculator. Answer all three questions.
Problem 1:
a:
Find the solution to the wave equation
satisfying
b: Describe qualitatively the solutions found in a:.
Problem 2:
a:
For which values of 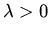 will
will
have solutions (other than 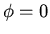 ) satisfying
) satisfying
b: Sketch the solutions for the three lowest values of 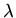 .
.
Problem 3:
The steady state temperature inside a bar satisfies the differential equation
The ends 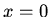 and
and 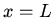 are kept at the temperatures
are kept at the temperatures 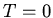 and
and 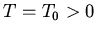 , respectively. The thermal conductivity depends on the temperature according to
, respectively. The thermal conductivity depends on the temperature according to
where 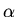 is a constant.
is a constant.
a: When integrating the steady state differential equation you will
end up with a quadratic equation for 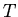 . Find this equation.
. Find this equation.
b: Solve this equation to
find the steady state temperature distribution 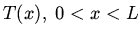 .
.
c: Which of the two
roots is correct when 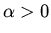 ?
?



Next: About this document ...
Birger Bergersen
2003-02-24